August 6, 2018
Versions in عربي, 中文, Español, Français, 日本語, Português, Русский
[caption id="attachment_24200" align="alignnone" width="1024"] The G7 countries, which are committed to the need for closing the gender gap, have a wage gap average of about 16 percentage points (photo: iStock by GettyImages).[/caption]
The G7 countries, which are committed to the need for closing the gender gap, have a wage gap average of about 16 percentage points (photo: iStock by GettyImages).[/caption]
In the battle for the parity of the sexes, some countries have made progress in reducing inequality—such as in access to health care, education, and financial services—but worldwide, men still have more economic opportunities than women.
Countries can fix the problem with the right policies that reduce the gender wage gap and level the playing field.
Our Chart of the Week, from the latest paper after the G7 Ministers and Central Bank Governors meeting, highlights these wage gaps. It measures the differences between men and women’s pay, and considers hours worked, type of employment, education levels, age and experience. Our chart shows that developing and advanced countries alike are in the same predicament.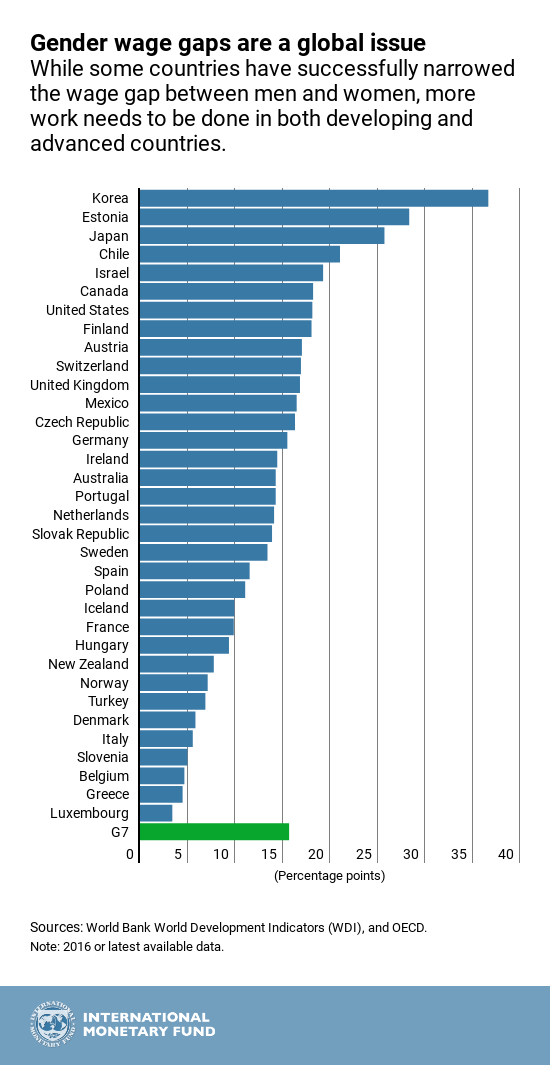
The chart shows that the wage gap is most pronounced in South Korea, which has a 37 percentage point difference in wages between men and women. The United States and Canada hover at around an 18 percentage point disparity, while Luxembourg comes in at the lower end of the scale, with a 3 percent point wage gap. The G7, which has emphasized and is committed to the need for closing the gender gap, has a wage gap average of about a 16 percentage points.
Gender inequality is directly linked to income inequality, which in turn can weaken the sustainability of growth in a country. Women getting paid less than men directly contribute to income inequality, and higher gaps in labor force participation rates between men and women result in inequality of earnings, unequal pensions and savings. Closing the gender wage gap can lead to greater equality in the overall income distribution.
The right policies can reduce the gender wage gap.
Overall, to reduce gender inequality and wage gaps, countries should focus on policies that improve education, health, infrastructure, increasing financial inclusion, and promoting equal rights.
In advanced economies and some developing countries, some of the policies that may help reduce wage gaps include:
- Offering publicly financed parental leave schemes. Long absences from the workforce to take care of children could lead to lower earnings upon return to work, as well as a reduced skill set.
- Removing the tax burden for secondary earners (mostly female). Replace family taxation with individual taxation.
- Use tax credits or benefits for low wage earners. These tax credits would reduce the net tax liability and increase the net income gain from accepting a job.




