“To truly be successful,

we should act together.

Cooperation remains the best way

to create a more prosperous future

for every nation.”
— CHRISTINE LAGARDE, MANAGING DIRECTOR

Building a Shared Future
IMF Annual Report 2018

International Monetary Fund Annual Report 2018
Message from the Managing Director
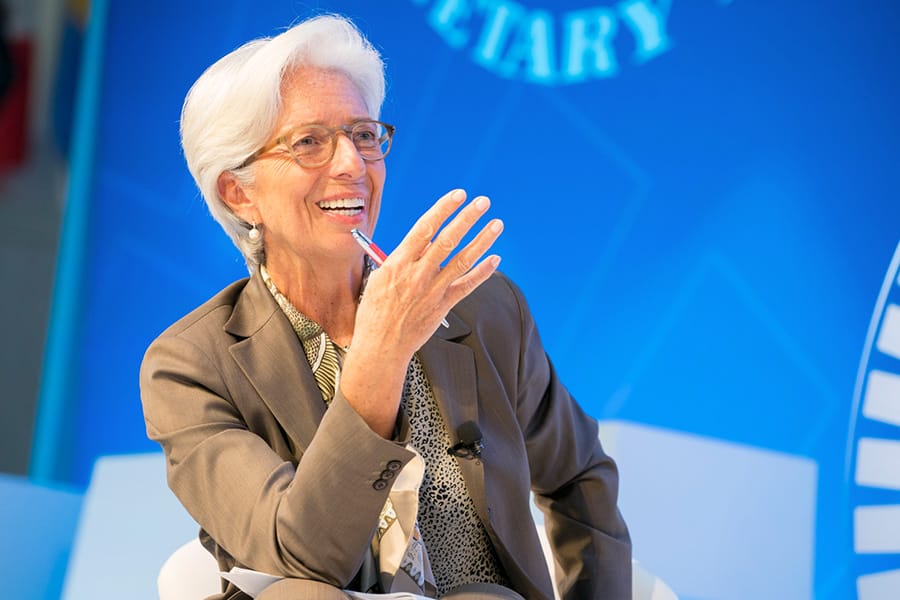

The global economic expansion we have seen over the past year has shown momentum, holding the promise of more jobs and improved living standards across most of our member countries. But there are threats, including from the risk of escalating trade conflicts, record high public and private debt, financial market volatility, and fragile geopolitics.
In the face of these challenges, my message to the membership has been and still is: the time to fix the roof is when the sun is shining. The window of opportunity is currently open. To keep momentum going, countries need to tame financial and fiscal risks by enhancing financial sector resilience and rebuilding policy space—and also need to make progress on the structural reforms that will strengthen the economy against any future storms. They should promote an open and rules-based multilateral trade system and should strive to make new technologies work for all—boosting rather than undermining inclusive growth and financial stability.
Looking more long term, global economic momentum is under pressure from a slow erosion/weakening of trust in institutions—and trust, of course, is the lifeblood of any economy. This faltering trust has many dimensions: the lingering effects of the global financial crisis, a perception that the rewards of economic growth and globalization are not being shared fairly, anxiety about the future of jobs and economic opportunity, and weak governance frameworks that too often facilitate corruption. Population aging and poor funding of pension schemes are also holding back momentum, and income disparities are widening. And, if unaddressed, climate change is likely to severely disrupt economic well-being in the decades ahead. Countries also must stay focused on these more slow-burning challenges.
As can be seen from this Annual Report, our Board of Executive Directors and staff are hard at work serving our members and helping them meet these challenges—in policy advice, in lending programs, and in capacity development. As just some examples, we have sought to strengthen crisis-prevention tools; refined the methodology to assess global imbalances and exchange rates; identified structural reform priorities to boost sustainable and inclusive economic growth, including in the area of gender equity and women’s labor force participation; enhanced our analysis of macro-financial and macrostructural issues; developed a new framework for tackling corruption and governance weaknesses; deepened our analysis of the digital economy and financial technology; and further stepped up our engagement on the Sustainable Development Goals.
As we face these uncertain economic times, I am convinced that the founding values of the IMF—centered on the idea that economic cooperation is the surest route to a better tomorrow—are more important than ever. Let us renew our commitment to these values.
About the IMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a global organization of 189 member countries set up to promote the health of the world economy. It works to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world. The IMF, which oversees the international monetary system to ensure its effective operation, has among its key purposes to promote exchange rate stability and to facilitate the expansion and balanced growth of international trade. The IMF’s mission enables countries (and their citizens) to buy goods and services from one another and is essential for achieving sustainable economic growth and raising living standards. All IMF member countries are represented on its Executive Board, which discusses the national, regional, and global consequences of each member’s economic policies and approves IMF loans to help member countries address temporary balance of payments problems, as well as capacity-building efforts. This Annual Report covers the activities of the Executive Board and IMF management and staff during the financial year May 1, 2017, through April 30, 2018. The contents reflect the views and policy discussions of the IMF Executive Board, which has actively participated in the preparation of this Annual Report.